Punnett Square
Definition
A Punnett Square is a tool used in genetics to predict the genotype and phenotype of offspring resulting from a specific cross between two parents. It was developed by Reginald Punnett and helps visualize all possible combinations of alleles that can be inherited from each parent, allowing for the calculation of probabilities for different traits.
Example
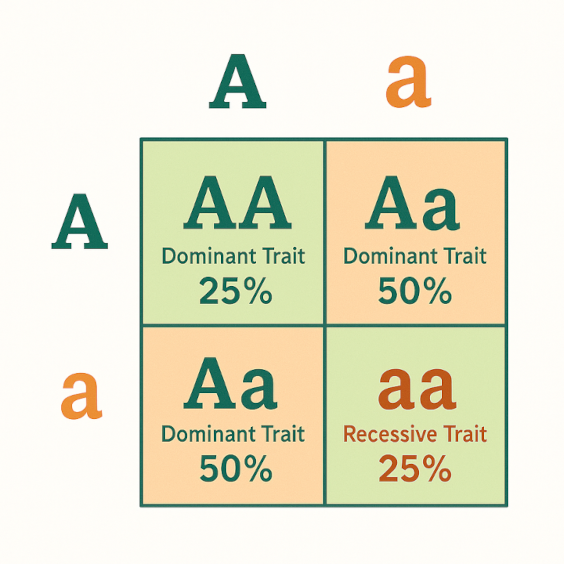
The image above illustrates a classic Punnett Square used to predict the probability of offspring inheriting particular traits from heterozygous parents (both carrying one dominant and one recessive allele: Aa).
In this example:
- Each parent contributes one allele to the offspring.
- The dominant allele is represented by A, and the recessive allele is represented by a.
When the alleles are combined in the Punnett Square:
- 25% of offspring are AA – displaying the dominant trait.
- 50% are Aa – also displaying the dominant trait, but carrying the recessive allele.
- 25% are aa – expressing the recessive trait, as two copies of the recessive allele are required.
This shows that even when both parents express the dominant trait, recessive traits can still appear in the next generation if both carry the gene.
Why it Matters
The Punnett Square is crucial in understanding genetic inheritance patterns and predicting the likelihood of specific traits appearing in offspring. This knowledge is vital in fields such as agriculture for selective breeding to enhance crop yields or disease resistance, in medicine for genetic counseling to assess hereditary disease risks, and in evolutionary biology to study trait distribution in populations. By providing a clear visual model, Punnett Squares enable researchers and students to grasp the principles of Mendelian genetics and apply them to real-world scenarios.